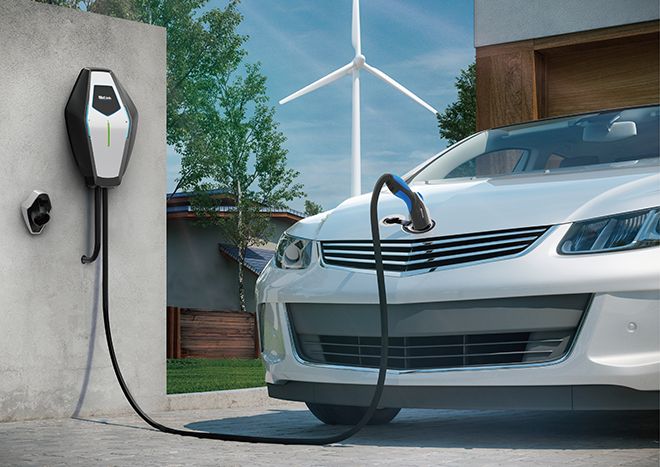
How are EV charging stations powered?
Without getting too technical, there are two types of electrical currents, and which one is used matters when it comes to EV charging: Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC).
Alternating current vs. direct current
Alternating current (AC)
The electricity that comes from the grid and is accessible through the domestic sockets in your home or office is always AC. This electrical current got its name because of the way it flows. AC changes direction periodically, so the current alternates.
Because AC electricity can be transported over long distances efficiently, it is the global standard we all know and have direct access to.
But that doesn’t mean we don’t use direct current. Quite the opposite, we use it all the time to power electronics.
The electricity that is stored in batteries or used in the actual power circuitry inside electric devices is direct current. Similar to AC, DC is also named after the way its power flows; DC electricity moves in a straight line and supplies your device with power directly.
So, for reference, when you plug an electric device into your socket, it will always receive an alternating current. However, batteries in electric devices store direct current, so the energy needs to be converted at some point inside your electrical device.
When it comes to power conversion, electric vehicles are no different. The AC power from the grid is converted inside the car by an onboard converter and stored in the battery as DC electricity—where it powers your vehicle from.
16A 32A RFID Card EV Wallbox Charger With IEC 62196-2 Charging Outlet
Post time: Dec-18-2023