About charging station
In 2011, the European Automobile Manufacturers Association (ACEA) defined the following terms:[2]
Socket outlet: the port on the electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE) that supplies charging power to the vehicle Plug: the end of the flexible cable that interfaces with the socket
outlet on the EVSE.
In North America, the socket outlet and plug are not used because the cable is permanently attached.
Cable: a flexible bundle of conductors that connects the EVSE with the electric vehicle
Connector: the end of the flexible cable that interfaces with the vehicle inlet
Vehicle inlet: the port on the electric vehicle that receives charging power
The terms “electric vehicle connector” and “electric vehicle inlet” were previously defined in the same way under Article 625 of the United States National Electric Code (NEC) of
1999. NEC-1999 also defined the term “electric vehicle supply equipment” as the entire unit “installed specifically for the purpose of delivering energy from the premises wiring to
the electric vehicle”,including “conductors … electric vehicle connectors, attachment plugs, and all other fittings, devices, power outlets, or apparatuses”.[3]
Tesla, Inc. uses the term charging station as the location of a group of chargers, and the term connector for an individual EVSE
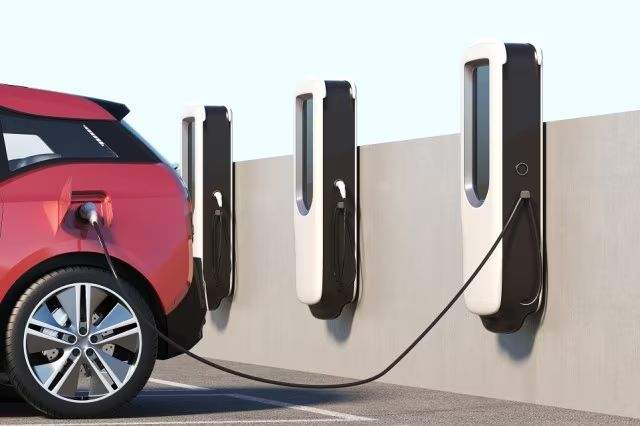
Alternating current (AC) AC charging stations connect the vehicle’s onboard charging circuitry directly to the AC supply.[8]
AC Level 1: Connects directly to a standard 120 V North American outlet; capable of supplying 6–16 A (0.7–1.92 kilowatts or “kW”) depending on the capacity of a dedicated circuit.
AC Level 2: Utilizes 240 V (single phase) or 208 V (three phase) power to supply between 6 and 80 A (1.4–19.2 kW). It provides a significant charging speed increase over AC
Level 1 charging.
11KW Wall Mounted AC Electric Vehicle Charger Wallbox Type 2 Cable EV Home Use EV Charger
Post time: Nov-21-2023